Adenocarcinoma colon in dogs
Adenocarcinoma Colon In Dogs. Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained. Occasional signs were weight loss vomiting and rarely diarrhea. Intestinal adenocarcinoma affects the cecum colon and mid-to-distal rectum of dogs. Identifying and treating anal sac adenocarcinoma in dogs.
 Intestinal Tumors Vca Animal Hospital From vcahospitals.com
Intestinal Tumors Vca Animal Hospital From vcahospitals.com
Intestinal tumors occur in older dogs median age 10 years. Adenocarcinomas are often classified as infiltrative expansile sometimes with ulcer formation polypoid nodularcobblestone and annular based on the biopsy and gross appearance. Dogs with apocrine gland adenocarcinoma treated with surgery and radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy have an average survival of over 25 years. Diarrhea and weight losswere associated with both colonic. In six of 10 dogs with rectal carcinoma rectal bleeding was seen and rectal prolapse occurred in one. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma and leiomyosarcoma are most common large intestinal tumors in dogs.
In dogs with colorectal neoplasms the most common clinical signs were straining on defecation and hematochezia. Ultrasonographic image of the descending colon in a Beagle later diagnosed with intestinal intraluminal papillary adenocarcinoma. Most of the dogs had clinical signs less than or equal to 12 weeks before examination. Colorectal adenocarcinoma was diagnosed in 78 dogs. Adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphoma are the most common canine intestinal tumors. Accordingly the aim of the present study is to report a case on infiltrative rectal adenocarcinoma diagnosed in a dog.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Colorectal neoplasia is an uncommon diagnosis in dogs. Adenocarcinoma and lymphoma are malignant tumors that make up nearly half of reported cases of colon cancer according to the National Canine Cancer Foundation. Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained. The most common gastrointestinal tumors in dogs are adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphosarcoma with adenocarcinoma being the most common. Identifying and treating anal sac adenocarcinoma in dogs.
 Source: scielo.br
Source: scielo.br
Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumour that originates from the epithelial layer of glandular tissue. Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumour that originates from the epithelial layer of glandular tissue. A 7-year-old male dog representative of the Fila Brasileiro breed was presented. Vet bills can sneak up on you. Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach Intestine or Rectum in Dogs This type of malignant tumor growth can take place in many parts of the body including the gastrointestinal system of dogs.
 Source: vcahospitals.com
Source: vcahospitals.com
The most common gastrointestinal tumors in dogs are adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphosarcoma with adenocarcinoma being the most common. Colorectal neoplasia is an uncommon diagnosis in dogs. This means that they spread to other organs. Adenocarcinoma 25 and lymphoma are most common large intestinal tumors in cats. It may invade any part of the gastrointestinal system including the stomach the small and large intestine and rectum.
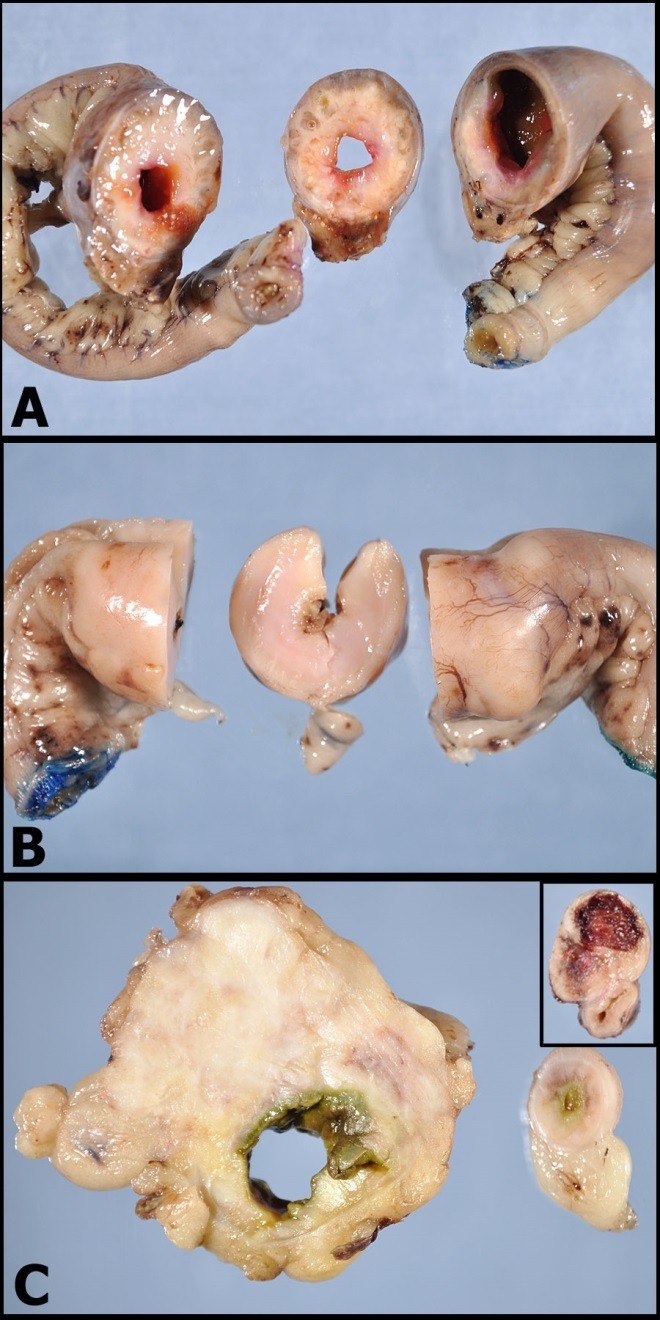 Source: mspca.org
Source: mspca.org
This intestinal neoplasia appears. A 7-year-old male dog representative of the Fila Brasileiro breed was presented. However colon cancer is serious and can have a poor prognosis. They are usually very aggressive and form often metastases. Intestinal adenocarcinoma affects the cecum colon and mid-to-distal rectum of dogs.
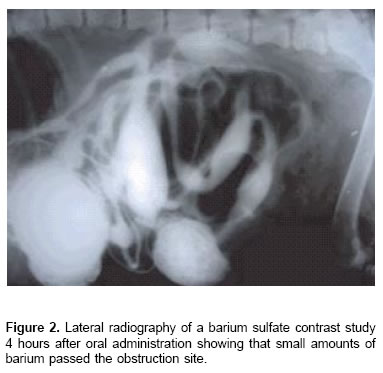 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
Accordingly the aim of the present study is to report a case on infiltrative rectal adenocarcinoma diagnosed in a dog. Other reported canine GI neoplasms include carcinoid adenoma leiomyoma carcinoma in situ and. Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors in dogs that can occur in different organs. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. Dogs with apocrine gland adenocarcinoma treated with surgery and radiation therapy followed by chemotherapy have an average survival of over 25 years.
 Source: vcahospitals.com
Source: vcahospitals.com
This intestinal neoplasia appears. Biopsy samples of colorectal polyps were collected and examined from 67 Miniature Dachshund dogs including 35 cases with an additional biopsy. Portion of the colon with loss of normal stratification of the intestinal layers and hyperechoic and heterogeneous echotexture Figure 1-B suggestive of neoplasia. Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors in dogs that can occur in different organs. This means that they spread to other organs.
 Source: vcahospitals.com
Source: vcahospitals.com
Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. Other large intestinal tumors include mast cell tumor and hemangiosarcoma. Identifying and treating anal sac adenocarcinoma in dogs. However colon cancer is serious and can have a poor prognosis. Adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphoma are the most common canine intestinal tumors.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
This intestinal neoplasia appears. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. However colon cancer is serious and can have a poor prognosis. It may invade any part of the gastrointestinal system including the stomach the small and large intestine and rectum. Less common tumor types include leiomyoma other sarcomas GISTs carcinoids plasma cell tumors and mast cell tumors.
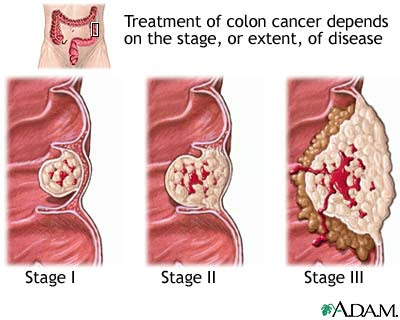 Source: contoh-soalsmp.blogspot.com
Source: contoh-soalsmp.blogspot.com
Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors in dogs that can occur in different organs. Adenocarcinoma is a malignant tumour that originates from the epithelial layer of glandular tissue. While intestinal cancer is rare in dogs most intestinal tumors are malignant and therefore prognosis is not good. Adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphoma are the most common canine intestinal tumors. Less common tumor types include leiomyoma other sarcomas GISTs carcinoids plasma cell tumors and mast cell tumors.
 Source: wagwalking.com
Source: wagwalking.com
Intestinal tumors occur in older dogs median age 10 years. Most of the dogs had clinical signs less than or equal to 12 weeks before examination. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. Identifying and treating anal sac adenocarcinoma in dogs. This means that they spread to other organs.
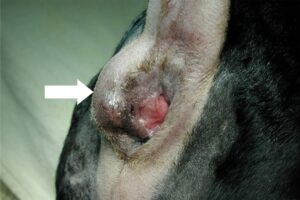 Source: bluepearlvet.com
Source: bluepearlvet.com
Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained. Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained. Adenocarcinomas are malignant tumors found in the glandular structures in the epithelial tissue. Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma and leiomyosarcoma are most common large intestinal tumors in dogs.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Most reports on colorectal neoplasia describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of dogs with adenocarcinoma. In six of 10 dogs with rectal carcinoma rectal bleeding was seen and rectal prolapse occurred in one. The most common gastrointestinal tumors in dogs are adenocarcinoma leiomyosarcoma and lymphosarcoma with adenocarcinoma being the most common. Colon Cancer in Dogs Explained. Adenocarcinoma and leiomyosarcoma are most common large intestinal tumors in dogs.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title adenocarcinoma colon in dogs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.