Sepsis infection in dogs
Sepsis Infection In Dogs. People sepsis in Veterinary Medicine is likely to be a major cause of mortality in hospitalized dogs and cats. Identifying Source of Infection A diagnosis of sepsis can be made once infection is documented and the patient fulfills the species specific criteria for SIRS Table 4. Appropriate samples Table 6 page 42 should. 1 Sepsis secondary to bacterial infection appears to be more common in dogs than viral or fungal sepsis.
 Sepsis And Septic Shock In Dogs Dunedin Animal Medical Center From dunedinamc.com
Sepsis And Septic Shock In Dogs Dunedin Animal Medical Center From dunedinamc.com
The main objective of the present study was to. The pathogen can also lead to other fatal. Sepsis causes a dog to feel very ill but the severity of the infection and what part of the body it is affecting will cause the symptoms of sepsis to vary. Sepsis secondary to parvoviral enteritis is also common though it is usually unclear whether the sepsis is truly viral in origin or secondary. Patients with SIRS andor sepsis should have a complete blood count serum biochemical profile urinalysis and coagulation testing performed. Sepsis develops if a dog is affected by an infection that is left untreated.
Sepsis in dogs is a life-threatening condition most likely caused by a bacterial infection but can also be caused by viruses fungi and protozoans.
Animals with SIRS frequently have concomitant organ injury or dysfunction that must be detected early in order to determine appropriate therapy monitor for changes and assist with prognosis. Sepsis develops if a dog is affected by an infection that is left untreated. For example if bacteria reaches the brain it can cause meningitis. Sepsis is more likely to develop in animals with a suppressed immune system or other immune disorder. Parvovirus enteritis is a predisposing factor for sepsis as it promotes intestinal bacterial translocation and severe immunosuppression. Forty-five dogs with sepsis 10 dogs with noninfectious systemic inflammation nSIRS and 15 healthy controls were consecutively enrolled from June 2015 to February 2016 and followed to hospital discharge.
 Source: todaysveterinarypractice.com
Source: todaysveterinarypractice.com
It is paramount for the dog to get a fast diagnosis and prompt treatment. 1 Sepsis secondary to bacterial infection appears to be more common in dogs than viral or fungal sepsis. Identifying Source of Infection A diagnosis of sepsis can be made once infection is documented and the patient fulfills the species specific criteria for SIRS Table 4. Sepsis an overwhelming infection in the body results in severe inflammation. Sepsis in dogs is a life-threatening condition most likely caused by a bacterial infection but can also be caused by viruses fungi and protozoans.
 Source: thesprucepets.com
Source: thesprucepets.com
Sepsis in dogs most commonly originates from the GI tract eg canine parvoviral enteritis followed by the respiratory tract eg bacterial pneumonia severe dental disease chronic urinary-tract disease and contaminated wounds. Sepsis secondary to parvoviral enteritis is also common though it is usually unclear whether the sepsis is truly viral in. This makes dogs infected by parvovirus a suitable study population as far as sepsis is concerned. But that wasnt the worst of it. If bacteria reaches the heart it can cause pericarditis.
 Source: wagwalking.com
Source: wagwalking.com
The remaining bone was completely flat as if someone had taken a large belt sander to the leg. It is paramount for the dog to get a fast diagnosis and prompt treatment. The remaining bone was completely flat as if someone had taken a large belt sander to the leg. According to DVM360 sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response to infection Sepsis in dogs typically originates in the gastrointestinal or respiratory tract. Sepsis and Septic Shock in Dogs.
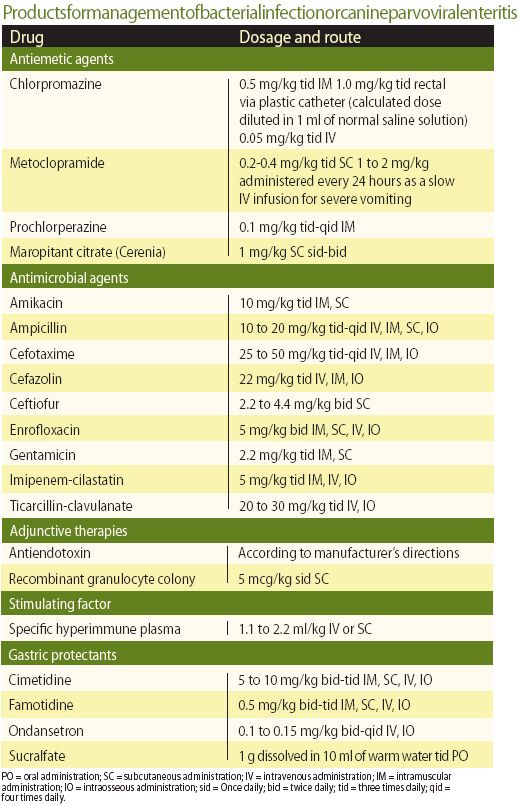 Source: dvm360.com
Source: dvm360.com
But that wasnt the worst of it. Untreated it can turn to severe sepsis which can cause multi-organ failure eg acute kidney failure acute respiratory distress syndrome or liver failure. Rarely nonbacterial infections can cause sepsis. If bacteria reaches the heart it can cause pericarditis. Appropriate samples Table 6 page 42 should.
 Source: merckvetmanual.com
Source: merckvetmanual.com
How can you tell if your dog has an infection. Sepsis is an infection which overwhelms the body resulting in severe inflammation. Without treatment it can escalate into Septic Shock causing multi-organ failure kidneys lungs liver. Here are the most common signs. Sepsis is the systemic inflammatory response to infection and carries a published mortality rate of up to 71 in the dog.
 Source: theveterinarynurse.com
Source: theveterinarynurse.com
Animals with SIRS frequently have concomitant organ injury or dysfunction that must be detected early in order to determine appropriate therapy monitor for changes and assist with prognosis. Septicemia in dogs is defined as the persistence of microorganisms or toxins in the bloodstream. People sepsis in Veterinary Medicine is likely to be a major cause of mortality in hospitalized dogs and cats. Animals with SIRS frequently have concomitant organ injury or dysfunction that must be detected early in order to determine appropriate therapy monitor for changes and assist with prognosis. Dog Diseases Conditions A-Z.
 Source: todaysveterinarynurse.com
Source: todaysveterinarynurse.com
Untreated it can turn to severe sepsis which can cause multi-organ failure eg acute kidney failure acute respiratory distress syndrome or liver failure. The pathogen can also lead to other fatal. According to DVM360 sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response to infection Sepsis in dogs typically originates in the gastrointestinal or respiratory tract. Sepsis in dogs most commonly originates from the GI tract eg canine parvoviral enteritis followed by the respiratory tract eg bacterial pneumonia severe dental disease chronic urinary-tract disease and contaminated wounds. Sepsis is the systemic inflammatory response to infection and carries a published mortality rate of up to 71 in the dog.
 Source: todaysveterinarypractice.com
Source: todaysveterinarypractice.com
Here are the most common signs. Sepsis is a severe condition associated with high prevalence and mortality rates. Sepsis causes a dog to feel very ill but the severity of the infection and what part of the body it is affecting will cause the symptoms of sepsis to vary. For example if bacteria reaches the brain it can cause meningitis. Identifying Source of Infection A diagnosis of sepsis can be made once infection is documented and the patient fulfills the species specific criteria for SIRS Table 4.
 Source: animalcareinfo.com
Source: animalcareinfo.com
Generalized body shaking weakness and confusion are commonly seen in dogs with sepsis regardless of what part of the body is most affected. Without treatment it can escalate into Septic Shock causing multi-organ failure kidneys lungs liver. Capnocytophaga canimorsus is a gram-negative bacterium which is found in the normal flora of the oropharyngeal tract of dogs and cats. If bacteria reaches the heart it can cause pericarditis. Animals with immune system disorders are more vulnerable to sepsis.
 Source: dunedinamc.com
Source: dunedinamc.com
Animals with SIRS frequently have concomitant organ injury or dysfunction that must be detected early in order to determine appropriate therapy monitor for changes and assist with prognosis. Forty-five dogs with sepsis 10 dogs with noninfectious systemic inflammation nSIRS and 15 healthy controls were consecutively enrolled from June 2015 to February 2016 and followed to hospital discharge. Generalized body shaking weakness and confusion are commonly seen in dogs with sepsis regardless of what part of the body is most affected. People sepsis in Veterinary Medicine is likely to be a major cause of mortality in hospitalized dogs and cats. Sepsis is less common than bacteremia and usually occurs when theres an infection at some other place in the body such as the lungs stomach or urinary tract.
 Source: wagwalking.com
Source: wagwalking.com
It is paramount for the dog to get a fast diagnosis and prompt treatment. Patients with SIRS andor sepsis should have a complete blood count serum biochemical profile urinalysis and coagulation testing performed. Sepsis an overwhelming infection in the body results in severe inflammation. Capnocytophaga canimorsus is a gram-negative bacterium which is found in the normal flora of the oropharyngeal tract of dogs and cats. Sepsis is an infection which overwhelms the body resulting in severe inflammation.
 Source: dogtime.com
Source: dogtime.com
Dog Diseases Conditions A-Z. Sepsis causes a dog to feel very ill but the severity of the infection and what part of the body it is affecting will cause the symptoms of sepsis to vary. According to DVM360 sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response to infection Sepsis in dogs typically originates in the gastrointestinal or respiratory tract. Sepsis is the systemic inflammatory response to infection and carries a published mortality rate of up to 71 in the dog. This makes dogs infected by parvovirus a suitable study population as far as sepsis is concerned.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title sepsis infection in dogs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





