Testicular cancer in dogs
Testicular Cancer In Dogs. It is well known that all dogs can contract testicular tumors though the underlying reason for the high rate is unknown. In-depth descriptions of these tumor types are discussed in this post. After neutering the dog the testicles may be sent out to a lab to determine whether they were cancerous or not. Interstitial Sertoli and seminoma tumors.
 Testicular Tumor Leydig Cell In Dogs Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost From wagwalking.com
Testicular Tumor Leydig Cell In Dogs Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Management Cost From wagwalking.com
In the long term neutering saves vets bills as neutered dogs are usually healthier and less likely. Testicular cancer is easily prevented through neutering at an early age. Since most dogs are neutered when they are very young though this cancer is generally rare. Testicular disease in dogs is more common for older canines than younger ones. Older cryptorchid dogs greater than 6 years of age have a much higher tendency to develop some form of testicular cancer. Hemangiomas granulosa cell tumors teratomas sarcomas and embryonal carcinomas.
Testicular cancer in dogs - There are three types of testicular tumors are common.
Interstitial Sertoli and seminoma tumors. Older cryptorchid dogs greater than 6 years of age have a much higher tendency to develop some form of testicular cancer. Sertoli cell tumors are a form of testicular tumor in dogs and are linked with undescended testicles. 1 seminoma 2 Leydig or interstitial cell tumor and 3 Sertoli cell tumor. Testicular cancer is easily prevented through neutering at an early age. These are seminomas sertoli cell tumours and interstitial cell tumours.
 Source: vosd.in
Source: vosd.in
Testicular tumors occur in male un-neutered dogs. Cancer can be described as a growth of cells in or on the body that has blown out of control. 1 seminoma 2 Leydig or interstitial cell tumor and 3 Sertoli cell tumor. Older dogs in general have a higher rate of developing these tumors. Sertoli cell tumors seminomas and interstitial cell tumors.
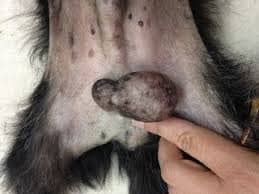 Source: urbananimalveterinary.com
Source: urbananimalveterinary.com
The majority of canine pets in the United States are immune to this disease entirely. Testicular cancer in dogs is relatively easy to resolve as the testes are outside of the body and can simply be removed with a short surgical procedure. Except for mixed breed dogs the Maltese breed had high detection rate of testicular tumors and may have high risk in cryptorchidism in this study. Testicular cancer is the most common form of genital cancer in male dogs. Can Dogs Get Testicular Cancer.
 Source: wagwalking.com
Source: wagwalking.com
Testicular cancer is easily prevented through neutering at an early age. This leads to decreased red blood cells bruising or abnormal white blood cells. Sertoli cell tumors seminomas and interstitial cell tumors. The detection rate of testicular tumors in the dog younger than 10-years-old was significantly associated with cryptorchidism p. Certain breeds of dogs may be more predisposed to the development of testicular tumors including Boxer Dogs German Shepherds Afghan Hounds Weimaraners Shetland.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
In the long term neutering saves vets bills as neutered dogs are usually healthier and less likely. Testicular cancer is the most common form of genital cancer in male dogs. Cancer can be described as a growth of cells in or on the body that has blown out of control. More than one of these three types can occur in one cancerous testicle and both testicles can be cancerous but have different types of testicular cancer. There are three main kinds of cancer that affect the testicles of dogs.
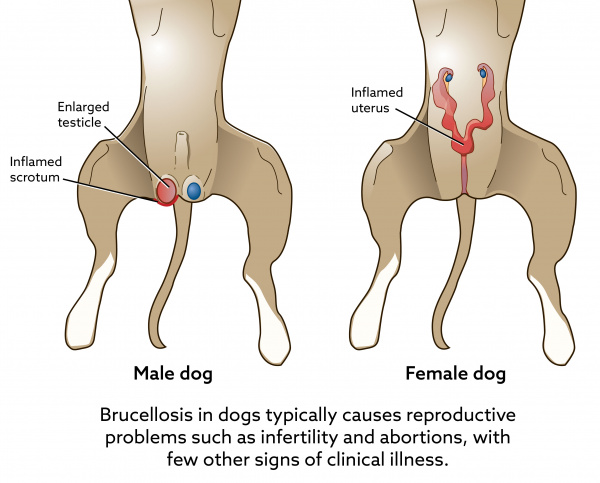 Source: vcahospitals.com
Source: vcahospitals.com
They also produce the widest range of symptoms. The most common forms include Leydig cell tumors LCT seminomas SEM and Sertoli cell tumors SCT. Testicular cancer in dogs is treated by neutering the dog. Cancer can be described as a growth of cells in or on the body that has blown out of control. Some symptoms could be linked to other diseases as well.
 Source: petcoach.co
Source: petcoach.co
Since most dogs are neutered when they are very young though this cancer is generally rare. Leydig also known as interstitial cell tumor Sertoli cell tumor. Sertoli cell tumors are considered to be the most common and the most serious form of testicular cancer in dogs. Some symptoms could be linked to other diseases as well. For male dogs that are not neutered testicular cancer is among one of the most common conditions.
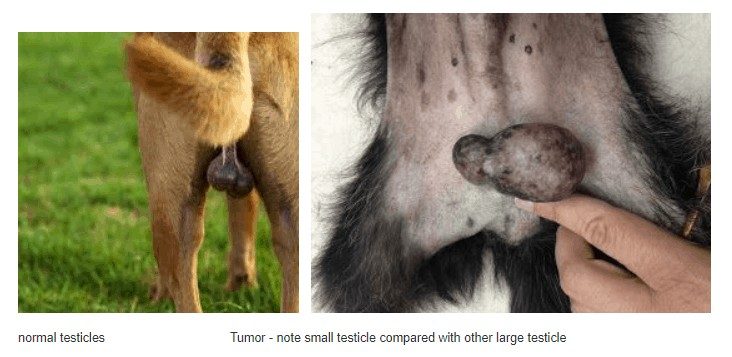 Source: urbananimalveterinary.com
Source: urbananimalveterinary.com
The overall incidence in dogs is not very high because of the large number of dogs that are castrated. Male dogs that have been neutered are at no risk of getting testicular cancer. Leydig also known as interstitial cell tumor Sertoli cell tumor. Occasionally when the cancer has metastasized the treatment required needs to be more aggressive and the prognosis more guarded with a longer recovery time for the affected dog. After neutering the dog the testicles may be sent out to a lab to determine whether they were cancerous or not.
 Source: healthierdogs.com
Source: healthierdogs.com
Testicular cancer in dogs is an unusual condition. Its thought that some cancer is caused by a variety of risk factors. Testicular tumors occur in male un-neutered dogs. Different types of testicular tumors. Sertoli cell tumors seminomas and interstitial cell tumors.
 Source: shutterstock.com
Source: shutterstock.com
Sertoli cell tumors are considered to be the most common and the most serious form of testicular cancer in dogs. Neutering in young dogs also prevents aggression roaming urine marking and a variety of other unwanted male behaviours. Some symptoms could be linked to other diseases as well. Background Testicular tumors are the most common genital neoplasms in male dogs with Leydig cell tumors LCT seminomas SEM and Sertoli cell tumors SCT the most common forms. Different types of testicular tumors.
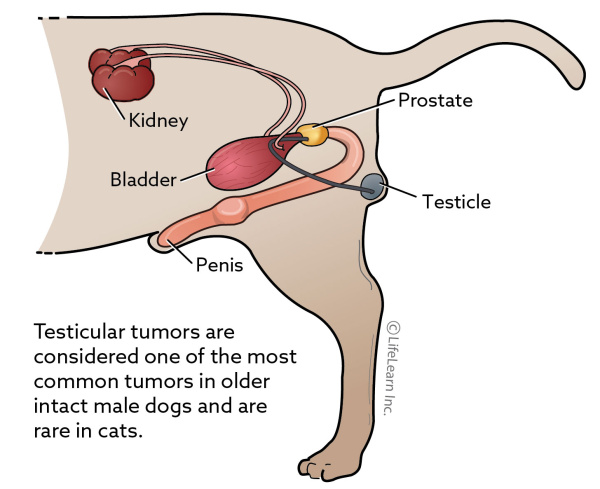 Source: vcahospitals.com
Source: vcahospitals.com
Neutering in young dogs also prevents aggression roaming urine marking and a variety of other unwanted male behaviours. Three types of tumors are grouped under the umbrella of testicular cancer. Since most dogs are neutered when they are very young though this cancer is generally rare. Different types of testicular tumors. Cancer can be described as a growth of cells in or on the body that has blown out of control.
 Source: animalsurgicalcenter.com
Source: animalsurgicalcenter.com
Sertoli cell tumors are considered to be the most common and the most serious form of testicular cancer in dogs. It is the second-most common cancer in intact older dogs. Testicular cancer is easily prevented through neutering at an early age. Cryptorchid dogs or those with undescended testicles have a greater tendency to develop testicular cancer. These are seminomas sertoli cell tumours and interstitial cell tumours.
 Source: biodataartissexy.blogspot.com
Source: biodataartissexy.blogspot.com
The most common forms include Leydig cell tumors LCT seminomas SEM and Sertoli cell tumors SCT. Although there are differences in the types of tumors they are often treated the same and which are therefore often lumped together as testicular tumors. Fortunately this type of cancer has a low rate for metastasizing spreading to other organs and therefore with the testicles removed there is usually no other treatment needed as the source. Although there is the possibility of a dog developing one type of tumor in one or both of the testicles theres also the possibility of the animal having two. Three types of tumors are grouped under the umbrella of testicular cancer.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title testicular cancer in dogs by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





